The NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart is a practical tool designed to help individuals track their blood pressure and pulse regularly. It aids patients in monitoring their health at home, ensuring accurate and consistent readings to manage hypertension effectively and improve overall well-being.
What is the NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart?
The NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart is a user-friendly PDF document designed to help individuals monitor and track their blood pressure readings over time. It provides a structured format with columns for date, time, systolic and diastolic values, and additional notes. This tool is particularly useful for patients with hypertension or those at risk of developing high blood pressure. By consistently recording readings, users can identify patterns, monitor progress, and share detailed information with healthcare professionals. The chart is printable, making it easy to use at home and during medical appointments. Regular use of the chart supports better blood pressure management and helps individuals take an active role in maintaining their cardiovascular health. It is a simple yet effective way to keep track of vital health data.
Why is Blood Pressure Monitoring Important?
Blood pressure monitoring is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications associated with hypertension. Regular tracking helps identify patterns and changes, enabling early detection of potential issues. Consistent monitoring allows individuals to assess the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medications, ensuring their blood pressure remains within a healthy range. By using tools like the NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart, patients can provide healthcare providers with detailed data, facilitating informed decision-making. Monitoring also empowers individuals to take proactive steps in managing their condition, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health problems. Accurate and frequent readings are essential for maintaining long-term well-being and preventing complications. This practice is vital for anyone diagnosed with high blood pressure or at risk of developing it. Regular monitoring supports overall health and ensures timely interventions when necessary. It is a simple yet vital habit for safeguarding cardiovascular health.
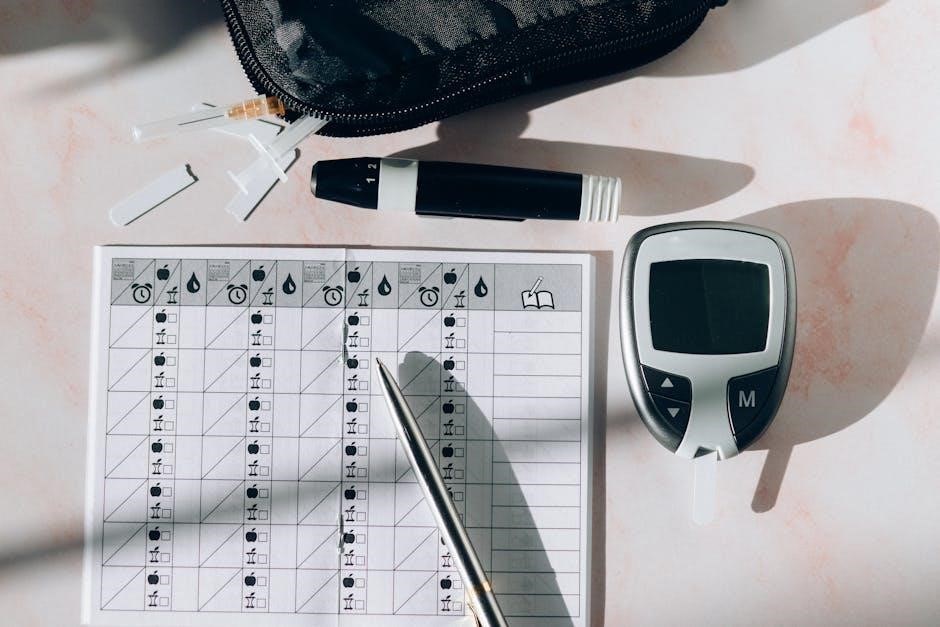
How to Use the PDF Printable NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart
Download and print the chart, then monitor and record your blood pressure and pulse rate twice daily, ideally for 7 consecutive days, to track trends and improvements effectively.
Downloading and Printing the Chart

To begin, download the PDF version of the NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart from the official NHS website or other trusted sources. Ensure your printer settings are configured to print the chart at the correct scale to maintain readability. Once printed, review the layout to familiarize yourself with the columns for date, time, systolic, diastolic, and pulse readings. Add your name, date of birth, and NHS number at the top for easy identification. For accurate tracking, record your blood pressure twice daily, ideally in the morning and evening, and note any relevant comments or symptoms. This organized approach helps healthcare professionals assess your progress and make informed decisions. Keep the chart handy and bring it to medical appointments for a comprehensive review of your blood pressure trends.
Understanding the Chart Layout
The NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart is designed with a clear and user-friendly layout to ensure accurate and organized tracking of your readings. The chart typically includes columns for the date, time, systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, and pulse rate, allowing you to record your blood pressure at specific intervals, such as morning and evening. Each row represents a single reading, making it easy to track changes over time. Additional sections may be provided for notes or comments, enabling you to document any factors that might influence your readings, such as physical activity, medication, or symptoms. The chart’s structured format helps healthcare professionals quickly assess your blood pressure trends and provide appropriate guidance. By following the layout, you can maintain consistency and clarity in your recordings, ensuring reliable data for better health management.
Step-by-Step Guide to Recording Blood Pressure
Prepare by resting for 5 minutes and sitting comfortably. Take two readings, one minute apart, while seated. Record date, time, systolic, diastolic, and pulse in the chart.
Preparing for Measurement
Before recording your blood pressure, ensure you are well-prepared to obtain accurate readings. Rest for at least 5 minutes in a quiet, comfortable environment. Avoid exercise, caffeine, or nicotine for 30 minutes prior to measurement. Sit in a relaxed position with your back supported and feet flat on the floor. Place your arm on a flat surface at heart level, with the cuff positioned correctly around your upper arm. Wear loose, comfortable clothing to ensure the cuff fits properly. Avoid talking or moving during the measurement, as this can affect the results. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your blood pressure monitor to ensure correct usage. Proper preparation helps ensure reliable and consistent readings, which are essential for effective blood pressure management. If unsure about any aspect, consult your healthcare professional for guidance.
Taking Accurate Readings
To ensure accurate blood pressure readings, use a validated monitor that fits your arm size. Place the cuff snugly, avoiding tight clothing that may interfere. Sit quietly, avoiding movement or conversation. Take two readings, one to two minutes apart, while seated comfortably. Record the systolic and diastolic values exactly as shown, along with your pulse rate if measured. If readings vary significantly, wait a few minutes and repeat. Note any symptoms or factors that might affect results, such as stress or recent activity. Consistency in timing, such as measuring at the same time each day, helps track patterns effectively. Always follow the monitor’s instructions and consult your healthcare professional if readings are consistently high or concerning. Accurate readings are crucial for proper blood pressure management and informed decision-making.
Entering Data into the Chart
When entering data into the NHS Blood Pressure Recording Chart, ensure accuracy and clarity. Record the date, time (morning or evening), and blood pressure readings in the designated columns. Include both systolic and diastolic values exactly as measured, avoiding rounding. Note your pulse rate if applicable. Use the notes section to document any factors that may influence readings, such as stress, exercise, or medication changes; Maintain consistency in recording to track patterns over time. Review entries regularly to identify trends or concerns. If unsure about how to fill in the chart, consult the provided instructions or seek guidance from a healthcare professional. Accurate and thorough documentation supports effective blood pressure management and informed healthcare decisions.

Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Readings
Compare systolic and diastolic values to assess your blood pressure category. Track trends over time to identify patterns and progress toward your health goals effectively.
Understanding Systolic and Diastolic Values
Your blood pressure reading consists of two values: systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number). The systolic value measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while the diastolic value measures the pressure when your heart rests between beats. A normal systolic value is typically below 120 mmHg, and a normal diastolic value is below 80 mmHg. Elevated or high readings may indicate hypertension, which can increase the risk of heart disease or stroke. Tracking these values helps identify patterns and monitor progress toward healthy goals. By regularly recording and analyzing systolic and diastolic values, you can better understand your blood pressure trends and work with healthcare professionals to manage your cardiovascular health effectively over time.
Setting Realistic Goals for Blood Pressure Management
Setting realistic goals is essential for effectively managing blood pressure. Aim to reduce your systolic and diastolic values gradually, ensuring sustainable progress. For example, if your readings are consistently high, a realistic target might be to lower your systolic value by 5-10 mmHg within 3 months. Incorporate lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction to support these goals. Monitor your readings regularly and adjust your targets as needed. Collaborating with your healthcare provider can help refine your objectives and ensure they align with your overall health. By maintaining consistent tracking and adhering to your goals, you can achieve better blood pressure control and reduce the risk of complications. Celebrate small achievements to stay motivated and focused on long-term wellness.